“2030年の未来都市創造のための超解像度都市センシング”を開催します!
開催日時: 2023 年 3 月 27 日(月) 13:30 ~ 17:30
開催場所: 慶應大学三田キャンパス 北館ホール
参加費: 無料 (どなたでもご参加頂けます)
参加申込はこちら から
【開催概要】
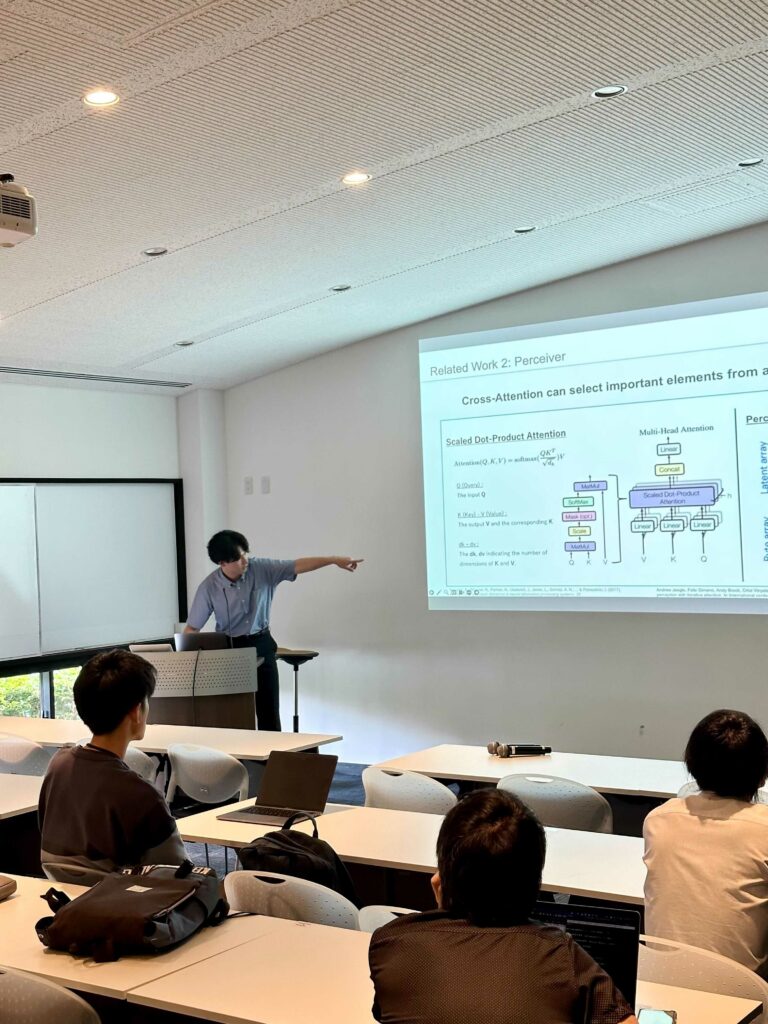
「地域IoTと情報力研究コンソーシアム」では、街のあらゆる情報を超解像度でセンシングする技術、Deep Learning画像分析をリアルタイムにエッジ処理する技術、また参加型センシングなど、あらゆる情報をハイブリッドに活用した超センサーフュージョン技術により、人の生活をより豊かにするスマートシティを構築するために、湘南地域の各自治体様とコンソ会員の各企業様、各大学研究室の皆様とともにいわゆる地域DX水平展開の活動を推進して参りました。また、このコンソーシアムの活動の中でいくつかの国プロの活動へも繋がり、昨年は特にNICTのBeyond5Gプロジェクトである「ShonanFutureVerse 」プロジェクトがスタートしました。ShonanFutureVerse 」プロジェクトとは、2030年のBeyond5Gの超高速、超低遅延、超多接続のネットワーク環境を最大限に活用し、現在都市の超解像度センシング技術と、交通、人流、環境、防災などのさまざまなユースケースにおける超精密シミュレーション技術とを組合せることによって、リアルな未来都市像を超精密かつリアルタイムに仮想空間上で可視化します。その際、未来都市像として、ワーストシナリオ(ヤバース)と、目指すべきシナリオ(キラバース)を具体的にビジュアル化し、この2つの未来都市像からバックキャスティングによって現在の人の行動がどうあるべきかを具体的に示唆することによって行動変容を促し、理想的な未来都市創造実現を目的とするプロジェクトです。実際に湘南地域の複数の自治体で交通、人流、環境、防災などのさまざまなユースケースにもとづく実証実験を行っていきます。
【主催】 地域IoTと情報力研究コンソーシアム
【共催】 Beyond 5G研究開発促進事業 委託研究 「ShonanFutureVerse 」プロジェクト一般社団法人 YRP研究開発推進協会
■プログラム
※本シンポジウム後には、懇親会を予定しておりましたが、参加希望者数が少ないため、大変恐縮ながら懇親会はキャンセルとさせて頂きます。既にお申込み頂いた方には大変申し訳ございません。
■基調講演
Photo. Muryo Honma (Rhizomatiks)
■ポスター展示者情報